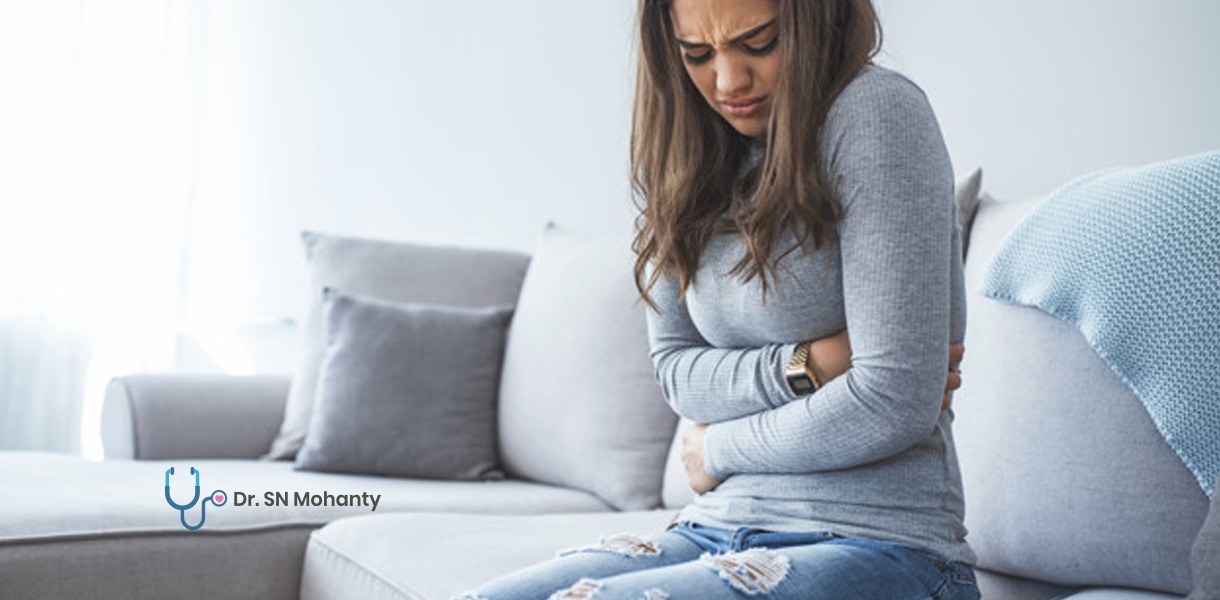
There are times when a patient is engrossed with multiple gynecological conditions. The symptoms of one gynecological condition may be severe and experienced, whereas symptoms of another one are not. Laparoscopic gynecological surgery such as laparoscopic cholecystectomy is occasionally done in conjunction with other intra-abdominal surgeries like laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy procedure, also called gall bladder removal surgery, is carried out to remove the gallbladder whereas laparoscopic salpingo-oophorectomy is done on the patient to remove ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Senior gynecologist like Dr. Suryanarayan Mohanty performs two surgeries in pair if and only if:-
• the surgical exposure is adequate
• the patient’s condition is satisfactory
• operating time is not much long
What is laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
It is a laparoscopic surgery that is performed to remove the gallbladder. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is less invasive than open one which needs a large incision in the patient's body.

.jpg)
The gallbladder is the organ of the human body that stores a substance called bile. It is in the shape and size of a small pear.
The gallbladder stores the bile in the body until the fatty food is completely digested in the human body.
Why laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
Gallstones are small crystals that form in the gallbladder. These crystals handle the blockage of the flow of bile in the digestive system causing inflammation of the gallbladder. This roadblock is called cholecystitis.
These gallstones also move to other parts of the body ad cause irritation. The laparoscopic specialist performs surgery to remove gallstones that are causing pain and infection in the patient's body.
Symptoms of gallstones include:
• Feeling bloated
• Fever
• Jaundice
• Nausea
• Pain in the right side of the abdomen may reach to the backside of the shoulder
What are the benefits of laparoscopic cholecystectomy?
The laparoscopic specialist removes the gallstones with laparoscopic cholecystectomy that is the removal of the gallbladder, with which the patient will not feel any discomfort or pain because of infection because of gallstones. If gallstones are not treated timely, they can be hazardous for the life of the patient.
Secondly, gallbladder removal surgery can also stop gallstones from coming back.
The gynecological doctor will perform certain tests to determine whether an open or laparoscopic type of surgery is suitable for the patient.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy provides the following benefits:
• less pain
• lower risk complications,
• quicker recovery so that the patient returns to routine life as soon as possible
• smaller wounds and scars,
Ovarian cystadenoma:
Ovarian cystadenoma is a type of pathological ovarian cyst.
An ovarian cyst occurs when fluid accumulates within a thin membrane inside the ovary of the patient.
Its structure is like a closed sac and varies in size from a pea to an orange. If the size of an ovarian cyst increases over 5 centimeters in diameter then it needs a surgical approach to be removed.
Ovarian cystadenoma is the type of ovarian cysts that grow in ovaries; they may be harmless or sometimes cancerous.
Cystadenomas are most commonly seen in women above 40 years of age. They develop to form the cells that cover the outer part of the ovary.
Some cysts are filled with mucus-like substances, whereas some contain watery liquid. Cystadenomas are usually attached to the ovary rather than growing inside it.

Symptoms of ovarian cystadenoma:
Some symptoms of ovarian cystadenoma resemble that of pregnancy. Other than this the symptoms include:
• Irregular and painful periods
• Pelvic pain that spreads to the lower back and thighs
• Bloating, swelling, or heaviness in the abdomen
• Problems in emptying the bladder or urinate frequently
• Pelvic pain during sexual intercourse or pain in the lower abdomen after sexual intercourse
• Pain or pressure during passing stools
• Hormonal abnormalities that affect breast size and hair growth
Sometimes bursting of cysts may cause severe pain in the lower abdomen of the patient. Also, in rare cases, they are an earlier form of ovarian cancer. Hence, your gynecological doctor may recommend you surgical approach as a treatment.
In some cases of cystadenomas, doctors prefer to carry out the surgical procedure called a salpingo-oophorectomy.
What is salpingo-oophorectomy and why it is done?
Salpingo-oophorectomy is a laparoscopic procedure to remove ovaries and fallopian tubes. It is a procedure that is used to treat a variety of gynecological conditions, including ovarian cancer.
This surgery is highly effective in reducing the risks of breast and ovarian cancer. Sometimes, to reduce the risk of cancer, experienced gynecological doctors like Dr. Surya Narayan Mohanty may remove healthy ovaries and fallopian tubes.
A patient can undergo a salpingo-oophorectomy procedure under the following gynecological conditions:
• Ovarian cancer
• Endometriosis
• Benign tumors or cysts
• Ectopic pregnancy
• Pelvic infection
It is one of the best, cost-effective as well as viable options to reduce the risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
Procedure:
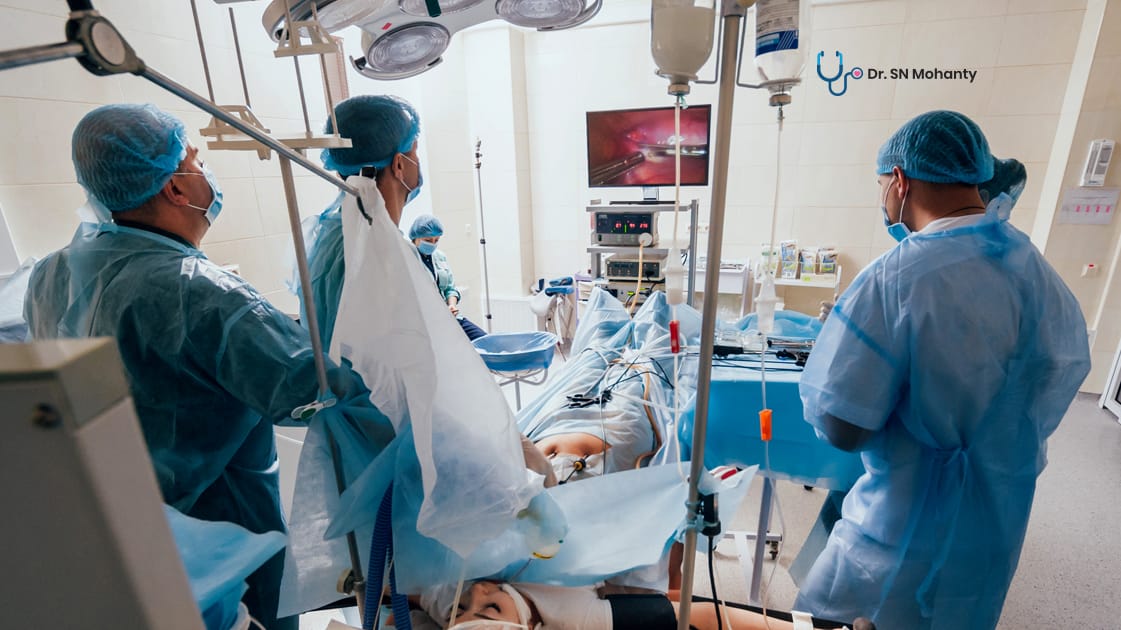
During laparoscopic surgery, the patient is given general anesthesia so that there is no pain during surgery.
A laparoscope is a thin lighted tube with a camera on one end.
The laparoscope during the surgery is inserted in the patient's abdomen through a small incision. A laparoscope is very thin, hence, it needs a tiny incision to be inserted.
The camera on one end sends the picture of the body parts in the pelvic organs on the TV monitor. It helps the laparoscopic specialists visualize the pelvic organs and precisely have access to ovaries and fallopian tubes with the help of surgical tools.
Ovaries and fallopian tubes are removed with the help of small incisions.
After the surgery is done the surgical instruments and laparoscope are carefully taken out and the incisions are stitched.
Recently Dr. Suryanarayan Mohanty handled the combined case of Laparoscopic cholecystectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy.
The case was:
Gall bladder stone with left-sided big cystadenoma of the ovary with stunting of two cardiac vessels.
The patient doesn't have symptoms of multiple gall bladder stones. The patient was having pain in the lower abdomen and heaviness in the lower abdomen. On USG, it was found; the patient had a gall bladder stone with huge ovarian cystadenoma.
 The patient had undergone earlier stenting or balloon angioplasty of two coronary vessels.
The patient had undergone earlier stenting or balloon angioplasty of two coronary vessels.
Dr. Suryanarayan Mohanty, being one of the senior laparoscopic surgeons in Bhubaneswar, successfully handled both the surgeries at a time and now the patient is healthy and has recovered after surgery.
Recovery after Laparoscopic cholecystectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy:
It may take some days or weeks to get recovered from the surgery and surgical wounds. Till then, you should make take complete rest and care of yourself. Following are some points that you should take into account regarding recovery after the procedure;
1. Right after recovery from anesthesia, nurses will check all your vital organs. You cannot leave the hospital till you can urinate on your own.
2. Recovery time varies from procedure to procedure. There are times you may need to stay for one or two nights in the hospital.
3. You may feel nauseated for the rest of the day after the procedure is performed.
4. As the carbon dioxide was filled in your stomach during the laparoscopy procedure, you may feel pain in your shoulder or chest.
5. Doctors will prescribe you some antibiotics and antibacterial ointments to get recover from the incision wounds.
6. You may be advised to avoid lifting heavy things few weeks after surgery.
Some risks related to the surgical procedure:
• Some side effects such as skin irritation and bladder infection are the most common side effects of surgery.
• Allergic reactions because some medications
• Adhesions
• Blood clots
• Difficulty in urinating
See your doctor immediately after surgery if;
• You experience serious abdominal pain
• Feel nausea for a long time
• You have a fever above 101⁰F
• Infection that is pus in your incision site
• You experience pain during urination and bowel movements