The human female reproductive system consists of various important elements. Every element is interlinked to each other and the function of every element is dependent on others. Five important internal organs of the female reproductive system are the vagina, uterus, fallopian pipes, cervix, and ovary. Ovaries as an important part of the female reproductive system are responsible for anatomically generating female egg cells.
They are also responsible for producing and secreting the female reproductive hormones- estrogen and progesterone. Ovaries are an internal part of the female reproductive system and are located in the lower abdomen. They are located on both sides of the uterus. Women have two ovaries that are oval and of the size of an almond. Sometimes, these ovaries develop cysts on their covering or inside them. Most of the women are found to have these cysts on their ovaries once in their lifetime.
Dr. SN Mohanty, one of the experienced gynecologists in Odisha, says that some of the ovarian cysts do not need any medication as women find no symptoms related to it whereas, women in some cases are seen have normal or severe symptoms regarding these ovarian cysts.
What are ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts fluid-filled sacs tend to develop on the ovaries of a female. Most of the women tend to have issues related to the ovarian cysts once in their lifetime. Some of them need treatment related to it whereas, some of them don't, depending on the type and size of the ovarian cysts.
Some of the women that develop ovarian cysts cause a condition called polycystic ovary syndrome. It is the condition in which there are many small cysts grown on the ovaries causing to grow the size of the ovary that leads to the root cause of their infertility.
Symptoms of the ovarian cysts:
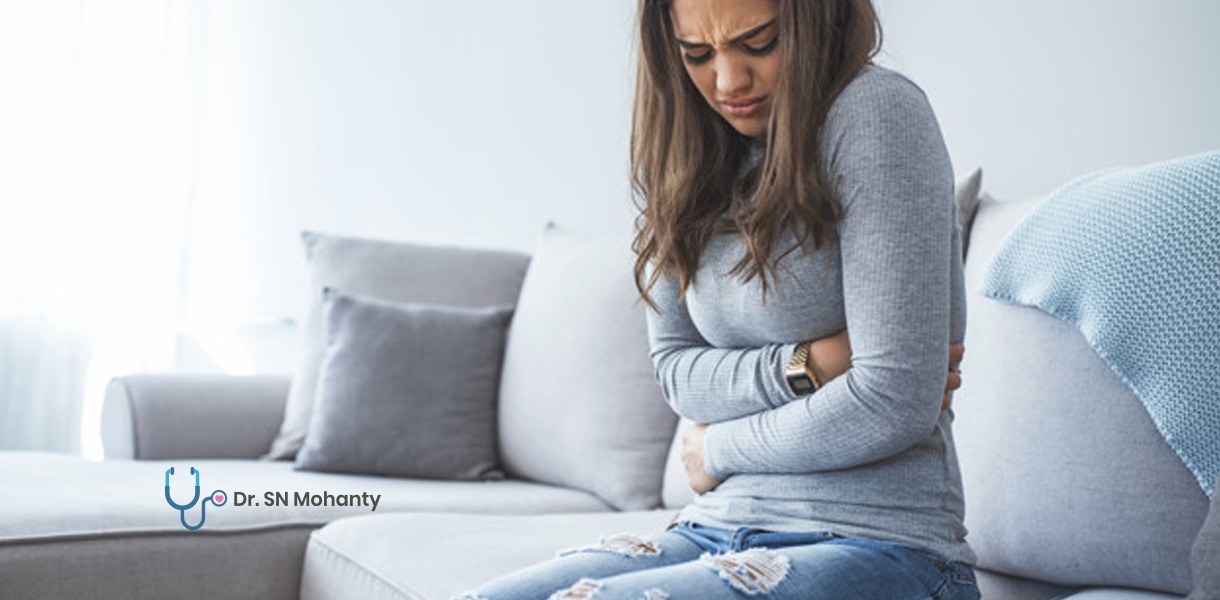
Some women do not feel any issue related to the ovarian cysts whereas, in some cases, they experience the symptoms like
• Mild to severe pain in the lower abdominal area
• Menstrual irregularities
• Nausea and vomiting
• Constipation
• Stomach bloating
• Painful periods, or a change in the pattern of periods
• A significant change in appetite
Some of the severe symptoms of ovarian cysts include conditions such as:
• Severe pain with fever
• Dizziness
• Sharp pelvic pain and rapid breathing
What are the complications regarding ovarian cysts?
Some of the ovarian cysts need no major treatment and get removed automatically. Whereas some of them which are non-cancerous, but needs to be treated. There are some cases where the ovarian cysts lead to major or immediate gynecological treatment with surgery. Dr. S. N. Mohanty, one of the best gynecologists has great and significant expertise in solving high-risk cases including the cancerous type of cysts.
What are the various ways to diagnose ovarian cysts?
There are various ways through which ovarian cysts can be detected. They are as follows:
• Through the routine pelvic examination
• An imaging test called ultrasound- with imaging tools such as CT scan, MRI, and ultrasound device
With imaging tests, the doctors can have a full view of the ovary and can detect and determine and size, shape, location, and composition of the ovarian cysts grown on the ovaries.
Doctors may use a wait-and-see approach as the majority of cysts may come and grow in a few weeks or few months. If there is no change in condition, then they may use the diagnosis ways such as
• Pregnancy test
• Hormone level test
• CA- 125 blood test to detect if the cysts are cancerous
What are the treatments for ovarian cysts?
Depending on the type and size of the ovarian cysts that have developed on the ovaries, the doctor will recommend you for the treatment. The doctor will recommend you to undergo the following treatments of the cysts are growing in size:
• Birth control pills:
Primarily doctors use the 'wait and see approach' to treat your cysts. After that, they will try the medication approach that is birth control pills. If the doctors see recurring ovulation through ovaries, then the doctor may prescribe you with the birth control pills to stop the ovulation of eggs from your ovary. Oral contraceptive pills are also used to prevent you from ovarian cancer that may be caused due to the growing ovarian cysts. Women are at higher risk of ovarian cancer in their menopausal period.
• Laparoscopy:
If the cyst on your ovaries is small and your doctor detects the least possibility of cancer, then he will perform laparoscopic cystectomy to remove ovarian cysts. It is one of the minimal access surgery that involves small incisions in your abdomen to remove the cyst.
• Laparotomy
In case you lave large size ovarian cyst on your ovaries, then the doctor will recommend you to undergo the laparotomy. It includes a large incision in your abdomen to remove cysts. Also, the doctor will include your treatment conducting an immediate biopsy and determine if the cyst whether it is cancerous or not. In case if the cyst is cancerous, then they perform a hysterectomy to remove the ovaries and in some cases removing the uterus.
How to prevent ovarian cysts?
Yes, ovarian cysts can be prevented. With routine gynecologic checkups, the doctor can determine ovarian cysts at an early stage. Indeed, cysts do not turn into cancerous ones, but in some cases, they are cancerous. Hence, it is important to visit the gynecologists in time to get proper diagnosis and advice. At Dr. S. N. Moanty’s clinic, you will get the best gynecological advice related to the ovarian cysts and what to do to prevent it.
The following are some piece of advice that will help you to prevent the ovarian cysts:
• Be alert with changes in your menstrual cycle
• Ongoing pelvic pain
• loss of appetite
• unexplained weight loss
• abdominal fullness
Though ovarian cysts do not turn into cancer, it is hazardous. If you are young and planning to be a mother, as most of the time they are responsible for a decrease in fertility. Hence, you should be alert and have a regular gynecologic checkup with your doctor. If you are near to your menopause period, in this case also, you should be alert with ovarian cysts as there is a possibility that they may grow cancerous.