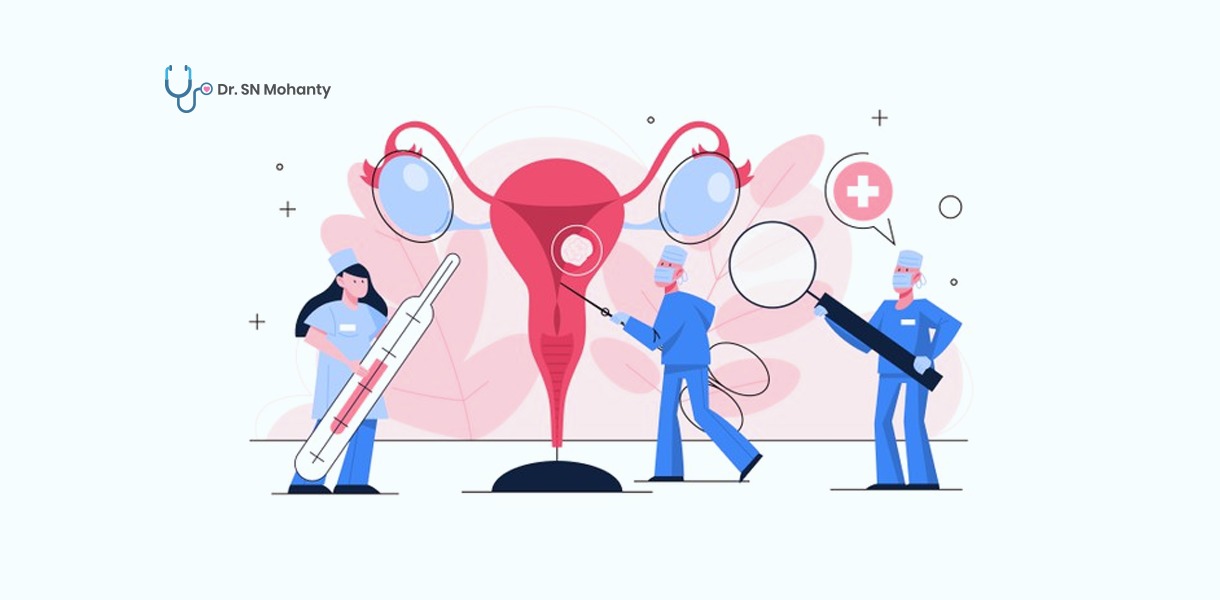
Hysterectomy is the surgery to remove a woman’s uterus. The uterus, otherwise called the womb, is the place a child develops when a woman is pregnant. The uterine coating is the source of menstrual blood.
You may require a hysterectomy for various reasons. The medical procedure can be utilized to treat various chronic pain conditions and also some types of cancer & infections.
The degree of a hysterectomy relies upon the explanation behind the medical procedure. Much of the time, the whole uterus is removed. The gynecologist may likewise eliminate the ovaries and the fallopian tubes during the surgery.
The ovaries are the organs that produce estrogen and different hormones. The fallopian tubes perform the function of transporting the egg from the ovary to the uterus. When you have a hysterectomy, you'll quit having from menstrual periods. You'll likewise be not able to get pregnant.
The major types of hysterectomy are:
• Supracervical hysterectomy is the process that involves the removal of the upper part of the uterus leaving the cervix.
• A complete hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus and cervix.
• A complete hysterectomy includes the removal of the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. On the off chance that you haven't encountered menopause, eliminating the ovaries will as a rule start it since your body can no longer create the required estrogen.
• A radical hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries, the upper portion of the vagina and some encompassing tissue, and lymph nodes. Radical hysterectomy is performed to treat cervical or uterine cancer.
Why is a hysterectomy performed?
A hysterectomy might is performed to treat:
• Abnormal vaginal bleeding that isn't controlled by other treatment techniques.
• Serious endometriosis (uterine tissue that develops outside the uterus).
• Uterine fibroids (non-cancerous tumors) that have grown in size, are very painful or are causing bleeding.
• Expanded pelvic pain related to the uterus however not constrained by other treatments.
• Uterine prolapse (uterus that has "dropped" into the vaginal trench because of weakened supporting muscles) that can prompt urinary incontinence or trouble with bowel movement.
• Cervical or uterine cancer or irregularities that may advance to cancer or to prevent cancer.
• Pelvic inflammatory disease
How is a hysterectomy performed?
A hysterectomy can be performed in various manners. It will rely upon your health history and the purpose behind your medical procedure. Have a word with your gynecologist about the different options available to you concerning your treatment.
The different options of hysterectomy are:
• Stomach hysterectomy: The doctor cuts typically in your lower abdomen.Vaginal hysterectomy. This is done through a little cut in the vagina.
• Laparoscopic hysterectomy: A laparoscope is an instrument with a dainty, lighted tube, and a little camera that permits your gynecologist to see your pelvic organs.
The laparoscopic medical procedure is the point at which the specialist makes exceptionally little cuts or entry points to put the laparoscope and surgical devices within you. During a laparoscopic hysterectomy, the uterus is removed through the little cuts made in either your mid-region or your vagina.
All of the above-stated treatment options require general or local anesthesia. An overall sedative will take care of you all through the surgery so you don't feel any pain. Local anesthesia will numb your body underneath the waistline, yet you'll stay awake during the medical procedure. This sort of anesthesia will be combined with a sedative, which will assist you with feeling sleepy and relaxed during the procedure.
Alternative to Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is the second most normal surgery performed on women. It's viewed as a protected and generally a low-risk surgery procedure. Be that as it may, a hysterectomy may not be the most ideal choice for all women. It shouldn't be performed on women who need to conceive except if there are different options are available.
Fortunately, numerous conditions that can be treated with a hysterectomy may likewise be treated in different manners. For example, hormone treatment can be utilized to treat endometriosis. Fibroids can be treated with different sorts of medical procedures that save the uterus.
In certain conditions, nonetheless, a hysterectomy is the most ideal decision. It's generally the main alternative for treating uterine or cervical cancer.
You and your gynecologist can examine your alternatives and decide the most ideal decision for your medical condition.
Recovery from Hysterectomy
After your hysterectomy, you'll have to go through two to five days in the medical clinic. Your gynecologist will give you medicines for the pain and screen your vital signs, for example, your breathing and pulse. You'll additionally be urged to walk around the medical clinic the soonest as possible. Walking prevents the formation of blood clots in the legs.
If you've undergone a vaginal hysterectomy, your vagina will be dressed with a bandage to control the bleeding. The doctors will eliminate the cloth inside a couple of days after the medical procedure. You may encounter bleeding or brownish discharge from your vagina for around 10 days.
At the point when you get back from the medical clinic, it's imperative to keep walking around. You can stroll around your home or your neighborhood.
You ought to restrain yourself from performing the following activities:
• pushing and pulling objects
• lifting heavy items
• twisting or bending
• sexual intercourse
If you've undergone a vaginal or laparoscopic hysterectomy, you'll likely have the option to be able to return to most of your regular activities. Recovery time will be somewhat more if you've had a stomach hysterectomy. You can be completely healed in about four to six weeks.